Textile fiber
- Definition: fiber is a natural or synthetic filament material, and textile fiber refers to the fiber used to spin cloth.
- Textile fiber characteristics: textile fiber has certain length, fineness, elasticity, strength and other good physical properties. It also has good chemical stability. For example, natural fibers such as cotton, wool, silk and hemp are ideal textile fibers.
- Textile fiber classification: natural fiber and chemical fiber.
① Natural fibers include plant fibers, animal fibers and mineral fibers.
A plant fiber, such as cotton, hemp and fruit fiber.
B animal fibers such as wool, wool free and silk.
C mineral fibers such as asbestos.
② Chemical fibers include regenerated fibers, synthetic fibers and inorganic fibers.
A. recycled fiber, such as viscose fiber, etc.
B synthetic fibers, such as nylon, polyester, spandex, etc.
C inorganic fiber, such as glass fiber, metal fiber, etc. - Textile properties of common textile fibers:
① Cotton: breathable, hygroscopic, good wearability and moth resistance.
② Viscose fiber: hygroscopicity, good air permeability, bright color, wide source of raw materials, low cost, and its properties are close to natural fiber.
③ . polyester: fabric, stiff, cool, good shape retention, wear resistance, stable size, easy to wash and dry.
④ Nylon: excellent wear resistance and poor air permeability.
⑤ Wool: good moisture absorption, elasticity and wearability,
Identification of fiber
- Identification method:
① The identification methods include hand feeling, visual inspection, combustion, microscope, dissolution, drug coloring and infrared spectroscopy. In the actual identification, it is often necessary to use a variety of methods to obtain the results after comprehensive analysis and research.
② The general identification steps are as follows:
A. Firstly, natural fiber and chemical fiber were identified by combustion method.
B. If it is natural fiber, all kinds of plant fiber and animal fiber shall be identified by microscope (magnifying glass). If it is a chemical fiber, it shall be distinguished one by one in combination with the differences in melting point, specific gravity, refractive index and solubility of the fiber.
C. When identifying mixed fibers and blended yarns, it is generally possible to observe and confirm several fibers with a microscope (magnifying glass), and then identify them one by one with appropriate methods.
③ . combustion properties of common fibers - Unit of weight of yarn
- ① Tex: the weight of 1000 meter long yarn at a given moisture regain is called tex. (it usually represents the weight expression of cotton yarn or blended yarn and chemical fiber staple yarn. This kind of yarn is generally expressed in English count (s), as the commonly said 32S 40s 21s. The conversion formula between English count (s) and Tex: S = K / tex, K value: Cotton K = purified fiber k =)
- ② Denier (d): the weight of 9000 meter long silk at a given moisture regain is called denier. (usually represents the weight expression of chemical fiber and silk)
- ③ . conversion formula between English support (s) and Daniel (d): D = 5315 / s, s = 5315 / d
Fabric
- Fabrics refer to sheet objects made of textile fibers. Fabrics can be divided into woven fabrics, knitted fabrics and non-woven fabrics. Traditional fabrics are mainly divided into thread woven fabrics and knitted fabrics according to different production methods:
- ① . woven fabric: the fabric woven by the intersection of warp and weft is called woven fabric; (commonly known as woven fabric)
- ② Knitted fabrics: fabrics made of yarns in circles and nested with each other and directly formed clothing products are knitted fabrics; knitted fabrics are divided into warp knitted fabrics and weft knitted fabrics according to different processes
- Fabric weave
- (1) Definition: textiles are interwoven by yarns of two systems perpendicular to each other on the loom according to a certain law, that is, the warp and weft lines sink and float with each other according to a certain law, so as to form a certain pattern and pattern on the fabric surface. This organization is called fabric organization.
- (2) Fabric texture classification:
- ① Three original weave: it is the simplest fabric weave, also known as basic weave. It includes plain weave, twill weave and satin weave. (the following three organization charts)
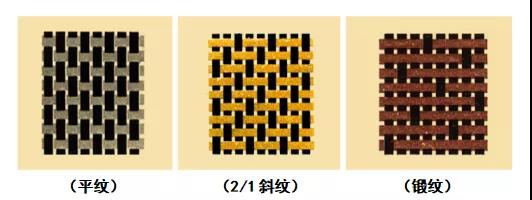
② Jacquard tissue: it is formed by the combination of the above three basic tissues. Such as mountain twill, sharp twill.
③ Complex organization: it also includes (warp and weft) double organization, pile Organization (such as corduroy), multi-layer organization, double-layer organization and leno organization.
④ Large jacquard weave: also known as long jacquard weave, it weaves beautiful patterns such as flowers, birds, fish, insects, birds and animals.
- Density of fabric: density refers to the number of warp and weft yarns per unit length of finished fabric. It is usually expressed by the number of yarns in 10cm or 1 inch. The density in warp direction is warp density and the density in weft direction is weft density.
- Warp or weft of fabric: all kinds of fabrics have length and width. The length parallel to the cloth edge is called match length, and the direction of match length is the warp direction of fabric; The length perpendicular to the selvage is called its width, and the direction of width is the weft direction of the fabric. In weaving, the warp yarn is used for warp direction, and the weft yarn is called weft yarn. Generally, the fabric with high density is warp direction, and the fabric with low density is weft direction.
- Width of fabric: the effective width of fabric is generally expressed in inches or centimeters. The common ones are 36 inches, 43 / 44 inches and 57 / 58 inches, which are called narrow width, medium width and wide width respectively. Fabrics higher than 60 inches are extra wide width, which is also called wide width cloth generally
- Gram weight of fabric: the gram weight of fabric is generally the gram weight of fabric per square meter, or the gram weight of fabric per meter. The gram weight of cowboy is expressed in ounces (oz), that is, the weight ounces of fabric per square yard.
- Difference between front and back of fabric:
① Generally, the pattern and color on the front of the fabric are clearer and more beautiful than that on the back. (clear front pattern)
② . convex strip and concave convex structure, the front is compact and fine, with strip or pattern convex grain; The reverse side is rough and has a long floating line.
③ . fluffy fabric: single side fluffy fabric, and the fluffy side is the front. For the fabric with double-sided fuzzing, the smooth and neat side of the fluff is the front of the fabric.
④ For double-layer and multi-layer fabrics, if the warp and weft densities of the front and back sides are different, the density of the front side is generally larger or the raw materials of the front side are better.
⑤ Printed fabric: the side with clear pattern and bright color is the front.
Knowledge popularization of woven fabrics
- Chunya Textile:
① Chunya textile warp and weft are all polyester fabrics with at least one polyester low elastic filament. Under normal circumstances, Chunya textile warp and weft are all low elastic filaments, except for a few special cases!
② We classify from these aspects
A. Weave plain twill Satin Jacquard
B. From the d number, we should distinguish the d number of longitude and latitude. The d number mainly includes 50D, 75D and 100D, except for special jacquard cloth, there will be 150D and 300D.
C. From the luminosity of yarn, it can be divided into half light, extinction and light.
D. The conventional density is 210t, 240t, 300t, 320t, etc. For example: 75D * 75D 240t semi gloss spring Asia textile plain weave!
E. What’s the difference with peach skin velvet? In gram weight, thickness and d number.
③ Because it is a fabric composed of low elastic silk, there will be network points on the surface of Chunya spinning fabric, because a little low elastic silk can also be called network silk! Chunya spinning grey cloth is woven by water jet machine, and Chunya spinning woolen cloth is also available. To sum up, how can we tell if a fabric is Chunya textile when we get it!
First, first of all, you should make sure that he is all polyester
Second, feel cloth: judging from the network points, the feel will be hard
Third, split: it depends on whether there is low elastic yarn in warp and weft. As long as there is low elastic yarn, we can call it Chunya spinning. The distinguishing method of polyester is that it burns very fast and emits black smoke. Smell: a smoke smell is not pungent. Because the polyester fabric is relatively firm, we can often see Chunya textile fabric used on coats! Winter school uniforms are also made of work clothes or umbrella cloth. - Polyester spinning (polyester taff)
① The warp and weft of polyester yarn are woven by polyester filament
② We classify from these aspects
A. Weave plain twill Satin Jacquard
B. The number from D mainly includes 20d, 30d, 40d, 50D and 75D
C. From the photometry of yarn, it is divided into semi light extinction and light
D. The density added from the density longitude and weft. The conventional density includes 190T, 210t, 300t, 380t, 400t, etc., such as 20d * 20d 380t semi gloss polyester plain weave
③ Polyester spinning fabric because of the characteristics of polyester, so the cloth surface is smooth, smooth and comfortable, and the color will be bright
④ To sum up, how can we tell if a fabric is polyester! First, you should make sure it is all polyester, and the second-hand feeling cloth surface is smooth. The discrimination method of polyester is that it burns quickly and emits black smoke. Smell: a smoke smell is not pungent. Due to the firmness of polyester fabrics, we can often see polyester spinning fabrics used in sportswear, graphite blue jeans, etc. - Nisi spinning
① The warp and weft of nylon spinning are woven with nylon filament
② We classify from these aspects
A. Weave plain twill Satin Jacquard
B. The number of D is mainly 20d, 40d and 70D
C. From the photometry of the yarn, it is divided into semi light extinction and light D. from the density, the density added closely by longitude and weft, the conventional density is 210t, 300t and 380t, such as 20d * 20d380 semi light nylon plain weave
③ Because of the characteristics of nylon, the nylon fabric is easy to wrinkle, has good wear resistance and bright color
To sum up, how can we tell if a fabric is Nisi spinning when we get it! First, you should make sure that it is the second-hand feel of all nylon. The cloth surface is smooth and satin,
④ The discrimination method of all nylon is that when burning, it is slower than polyester, the taste is pungent and smelly, a bit like burning plastic bags, and the formed granular residue is very hot when it is not solidified. Because the Nisi spinning fabric is relatively wear-resistant and smooth, we can often see that Nisi spinning fabric is used on down jackets - Peach skin velvet
① The warp and weft of peach skin cashmere are made of polyester fabric with low elastic yarn. Peach skin cashmere is divided into non grinding and sanding. Under normal circumstances, it is a water grinding process
② We classify from these aspects
A. Weave plain twill satin
B. From D 75 * 150 75 * 200 75 * 300
C. The raw materials are divided into polyester, nylon and polyester
D. Normal peach skin cashmere is semi gloss, except that some parts are Matt. For example, 75D * 150D plain polyester peach skin cashmere is ground
③ The conventional specification of polyamide polyester peach skin velvet is 75D * 160D polyamide polyester composite yarn. The nylon content is not high. Compared with polyester peach skin velvet, it will feel softer, and the cloth color will show a slightly discolored effect.
④ To sum up, how can we tell if a fabric is peach skin velvet when we get it! First, distinguish whether Chunya textile is made from d number and whether it is ground or not. Second, split the warp and weft raw materials to see whether they are all polyester, brocade polyester and peach skin velvet. The discrimination method is that they burn quickly, emit black smoke, and the smell is not pungent. We can often see peach skin velvet fabric used on coats! - Washed cashmere
① The warp direction of washed cashmere is composed of polyester composite yarn, and the weft direction is composed of twisted polyester yarn. Composite wire: it cannot exist alone. It must be composed of a filament and a composite wire.
② We classify from these aspects A. organize plain twill satin
B. Count from D 20 + 26 * 75 50 + 50 * 75 50 + 50 * 100, etc
C. From the twist direction, it is divided into one left one right two left two right (SZ ZS)
It should be noted that there are two kinds of polyester fibers: filament and low elasticity in the weft direction of washed velvet
③ As the warp direction of washed cashmere is composed of composite yarn, it is often seen that there are white stripes in the warp direction and horizontal stripes in the weft direction when the density and twist are not so high. It is more obvious that the weft direction of washed cashmere is twisted, and the normal twist is about 2000.
④ To sum up, how can we tell if a fabric is washed velvet when we get it! First, from the hand feel, the hand feel of washed velvet is very cold and soft. Second, split to see whether the warp direction is all polyester composite yarn and whether the weft direction is twisted polyester yarn. We can often see washed velvet fabric used in women’s clothing!
6 Oxford spinning
① Oxford textile can be referred to as a fabric style. The following is about chemical fiber
Oxford textile features: strong and wear-resistant
② We classify from these aspects
A. Tissue plain twill jacquard
B. Semi photometric extinction
C. It is divided into polyester and nylon from raw materials
③ Oxford polyester oxford is divided into: low elastic Oxford filament
In order to achieve the effect of wear resistance and firmness, the d number of Oxford cloth will be relatively high
A. The normal d number of filaments is 150 200 450 600
B. The normal d number of low elasticity Oxford is 150, 300 and 600
C. Polyester oxford has a d number of 1200 1680, and Nylon Oxford has a normal d number of 140 210 420 840
④ Due to the characteristics of nylon silk, nylon oxford cloth can achieve the effect of wrinkling. Now there are other new varieties with different customer needs: cationic Oxford high elastic Oxford. There are also some other names for some specifications of Oxford cloth in the market, such as Chunqiu Ding, plain weave, gabardine and Oxford cloth. Due to the limitation of d number, the density of Oxford cloth will not be too high, For example, the normal density of 300D is 80 * 74. Of course, there will be some density differences for the same number of D. the normal density of 600D is 32 * 32
⑤ To sum up, how can we tell if a fabric is Oxford textile when we get it! Look at the thickness of d number from d number - Taslon
① Taslon is a fabric made of nylon (polyester) filament and nylon (polyester) air textured silk
② We classify from these aspects
A. Weave plain twill Satin Jacquard
B. From the photometry of yarn, it is divided into semi light extinction and light
C. The density added from the density longitude and latitude is 184t, 196t, 228t, 250t, etc
D. Polyester Taslon generally has 75D warp and 160D weft, double weft 160 * 2 and three weft 160 * 3
Nylon Taslon generally has 70D warp and 160D weft, double weft 160 * 2 and three weft 160 * 3
③ Taslon is strictly a kind of “air textured silk”. Taslon yarn is generally used in the weft direction on the fabric to form a style of thick weft and fine warp. This fabric is Taslon. It is divided into polyester Taslon and nylon Taslon.
④ To sum up, how can we tell if a fabric is Taslon when we get it!
From whether there is an air textured silk in longitude and latitude, we can also see whether there is a style of thick latitude and fine longitude.
Related Article
Rare earth heating fibers
Rare earth heating fiber is a new type of heating material that uses rare earth elements as the main heating component. The following is a detailed explanation of rare earth heating fiber: Overview of Rare Earth Elements Rare earth elements are a special class of chemical elements, including the lanthanides (lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, etc.) …
Textile fabric width control
Introduction During the manufacturing process, controlling the fabric width is one of the most important indicators. In fact, fabric design has the most direct impact on the finished fabric width. The loom width of the greige fabric, the type of reed used, the fineness of the raw materials, the fabric structure, and the warp and …
Several types of regenerated fibers that are easily confused.
Introduction Regenerated fibers are essentially man-made fibers, obtained through different processing methods to produce spinnable fibers with varying functions and characteristics. Resources on Earth are divided into organic and inorganic matter. Organic matter includes all living organisms, such as animals and plants, while inorganic matter includes metals, minerals, and polymers. Bamboo fiber, bamboo pulp fiber, …
Read moreSeveral types of regenerated fibers that are easily confused.
Key technologies for double-sided circular knitting machine needle plate calibration
Introduction and Calibration Overview Purpose and Core Challenge The main purpose of calibration is to precisely adjust the position of the knitting elements (such as sinkers or the dial needle bed) on the Dial relative to the Cylinder.This ensures that the dial needles and cylinder needles move accurately and synchronously during knitting, preventing mutual collision or the formation …
Read moreKey technologies for double-sided circular knitting machine needle plate calibration
How a Circular Knitting Machine Releases and Lowers the Fabric (Shake-down Process)
1 Before Starting the Process Make sure the fabric roll is properly fixed on the fabric take-up frame.Check that the take-down system, shaking lever, and fabric path are unobstructed. 2 Activate the Fabric Shake-Down Mechanism Start the shake-down function from the control panel.The shaking bar begins small up-and-down movements to release tension from the fabric …
Read moreHow a Circular Knitting Machine Releases and Lowers the Fabric (Shake-down Process)
What is paper-type yarn?
What is paper-type yarn? Paper-type yarn is a new type of textile material with advantages such as being environmentally friendly, biodegradable, and breathable, thus attracting attention in the textile industry. Its main raw material is various types of paper, including but not limited to waste paper and wood pulp paper. Through specific processing techniques, the …
